What motivates people to undertake development service?
Motives for undertaking service
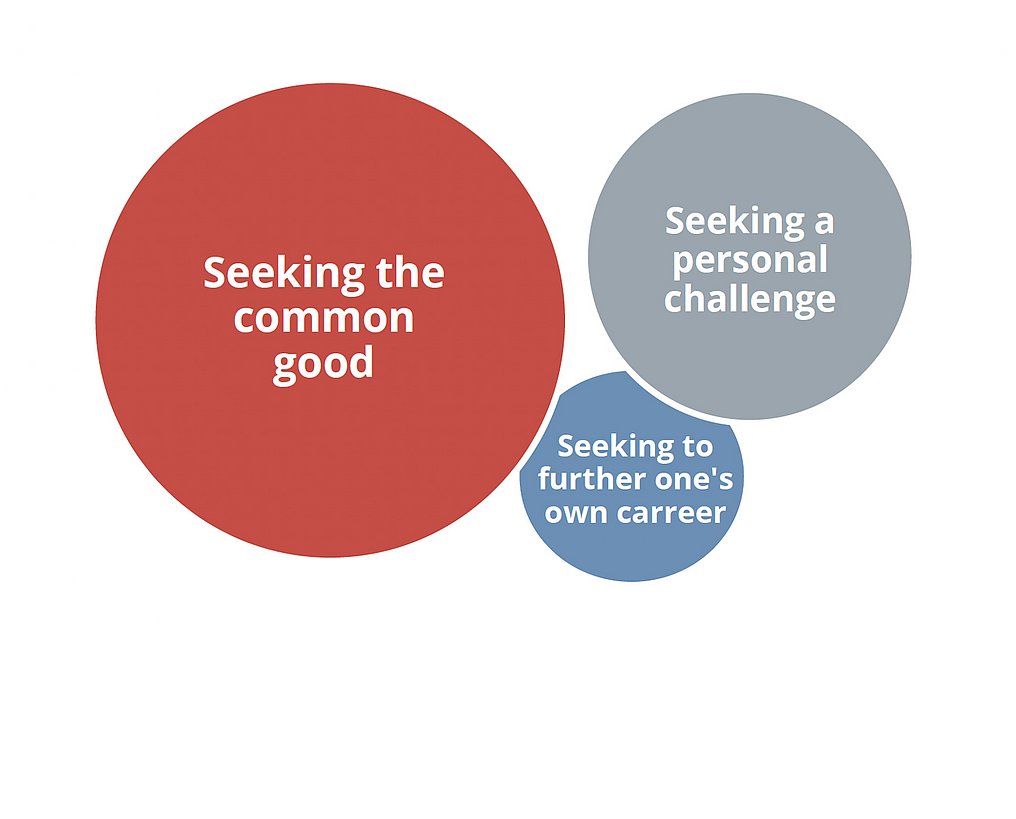
For most professional development workers, "seeking to promote the common good" was the most important factor in their decision to undertake development service or civil peace service.
“Seeking to promote the common good” means seeking:
- to promote justice and peace,
- to act in solidarity with people in the Global South,
- to do meaningful work, and
- to work in partnership with other people to create solutions.
These are the most important motives equally for both women and men and for all professionals, whichever sending agency they are with.
The second most important motivating factor is wanting to take on a "personal challenge". This might include:
- relating to other cultures,
- living and working abroad,
- opening oneself up to a new experience.
For most professionals in development service, furthering their career is less important as a motive for undertaking service.
The German Development Workers Act
When the Development Workers Act (EhfG) was passed in 1969, the idea of solidarity played an important role.
The Act states: "For the purposes of this Act, a development worker is defined as a person who renders service in a developing country without receiving a customary salary in order to contribute to the progress of such countries through cooperation in a spirit of partnership..."
Although development service requires excellent professional skills and experience, it is impossible to imagine that it could be undertaken without empathy or devoid of a spirit of solidarity. Professional workers in development service and the Civil Peace Service work in partnership with people and organisations to overcome poverty, protect natural resources, advance political reforms, and promote peace.
Results
Next: Civic engagement and development service
Where do professionals choose to live after they have completed their service?
How to make a success of returning home – both for yourself and for your family
Career paths after development service
Development service as a qualification – What skills do professionals bring from their service?
How development service affects your future career
Civic engagement – Before and after development service
In-depth interviews about the study
As part of the AGdD study 2022 "Before and after development service: A quantitative study among returnees (2011-2020) in-depth interviews were conducted with some study participants. They talked about their experiences, motivations for a development service and its influence until today - e.g. in the form of social engagement after their return.